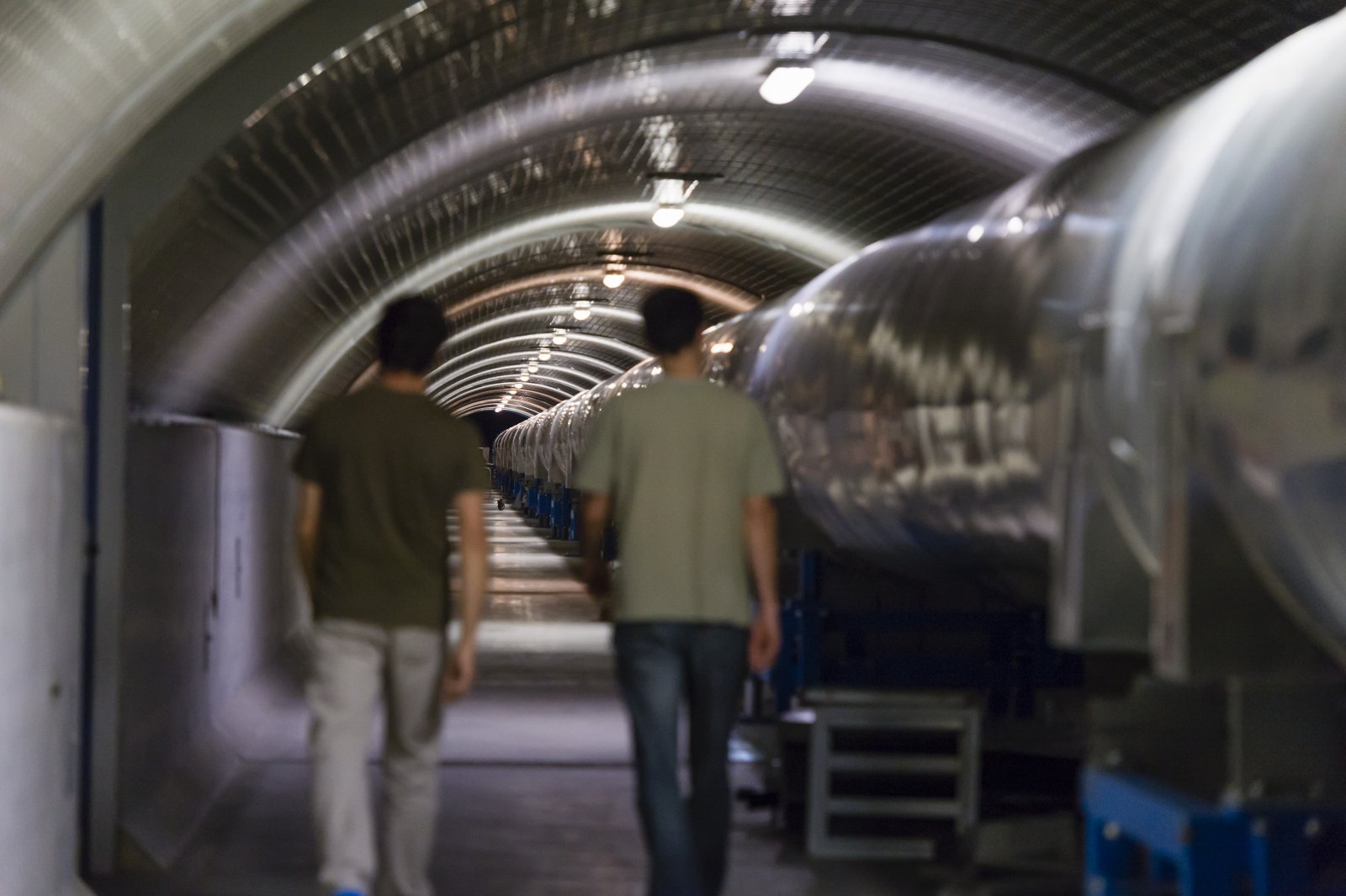
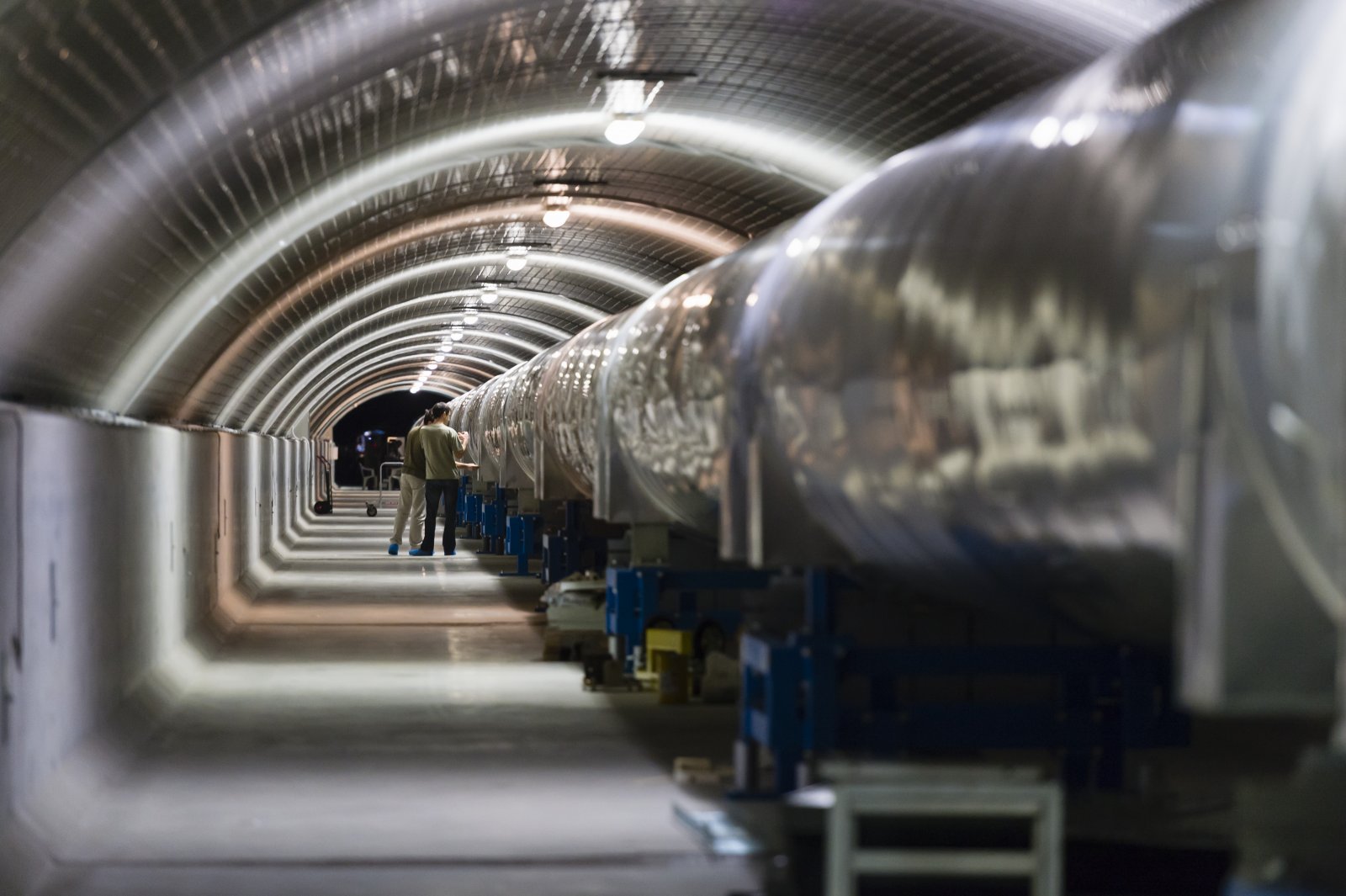
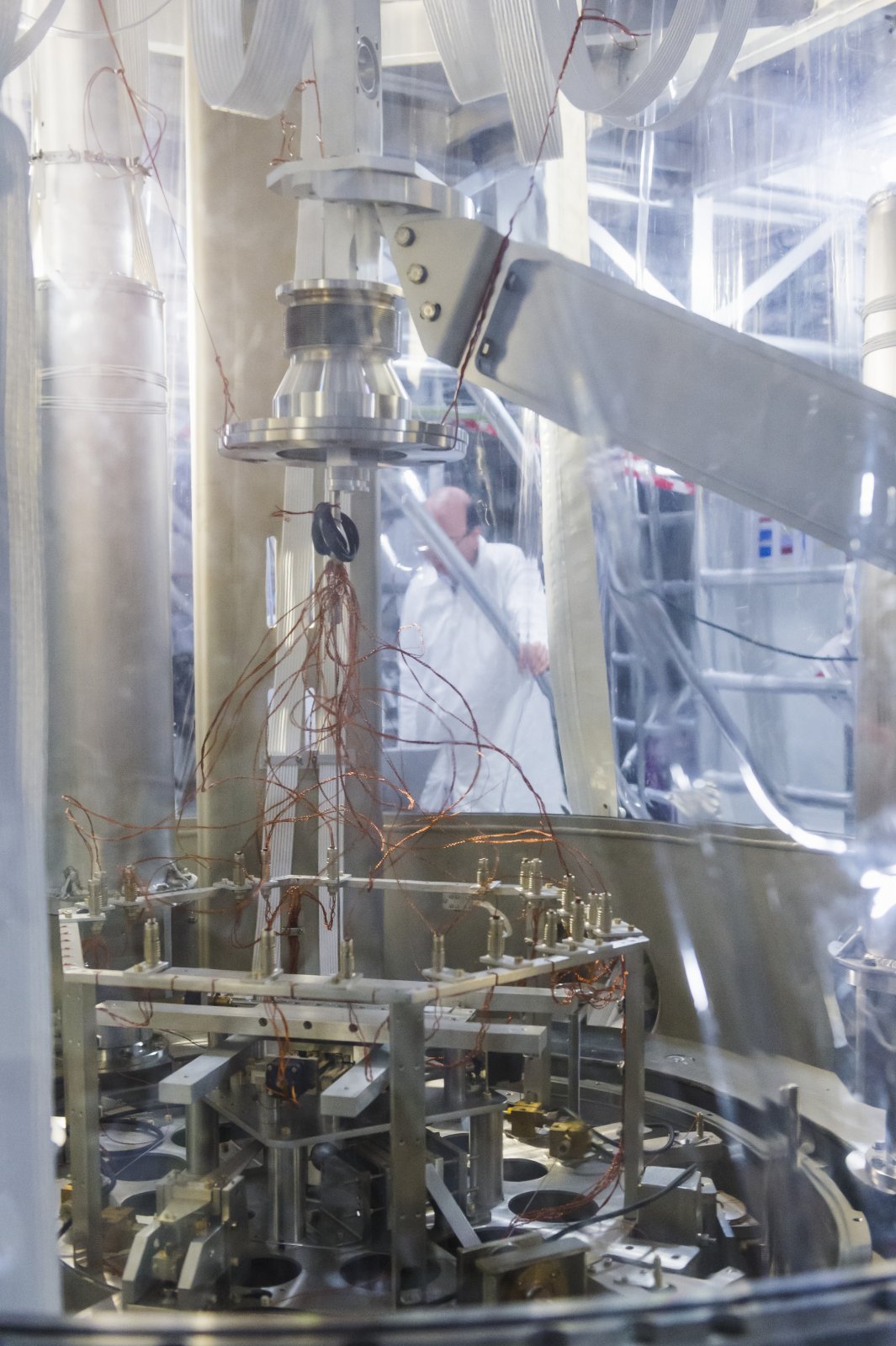
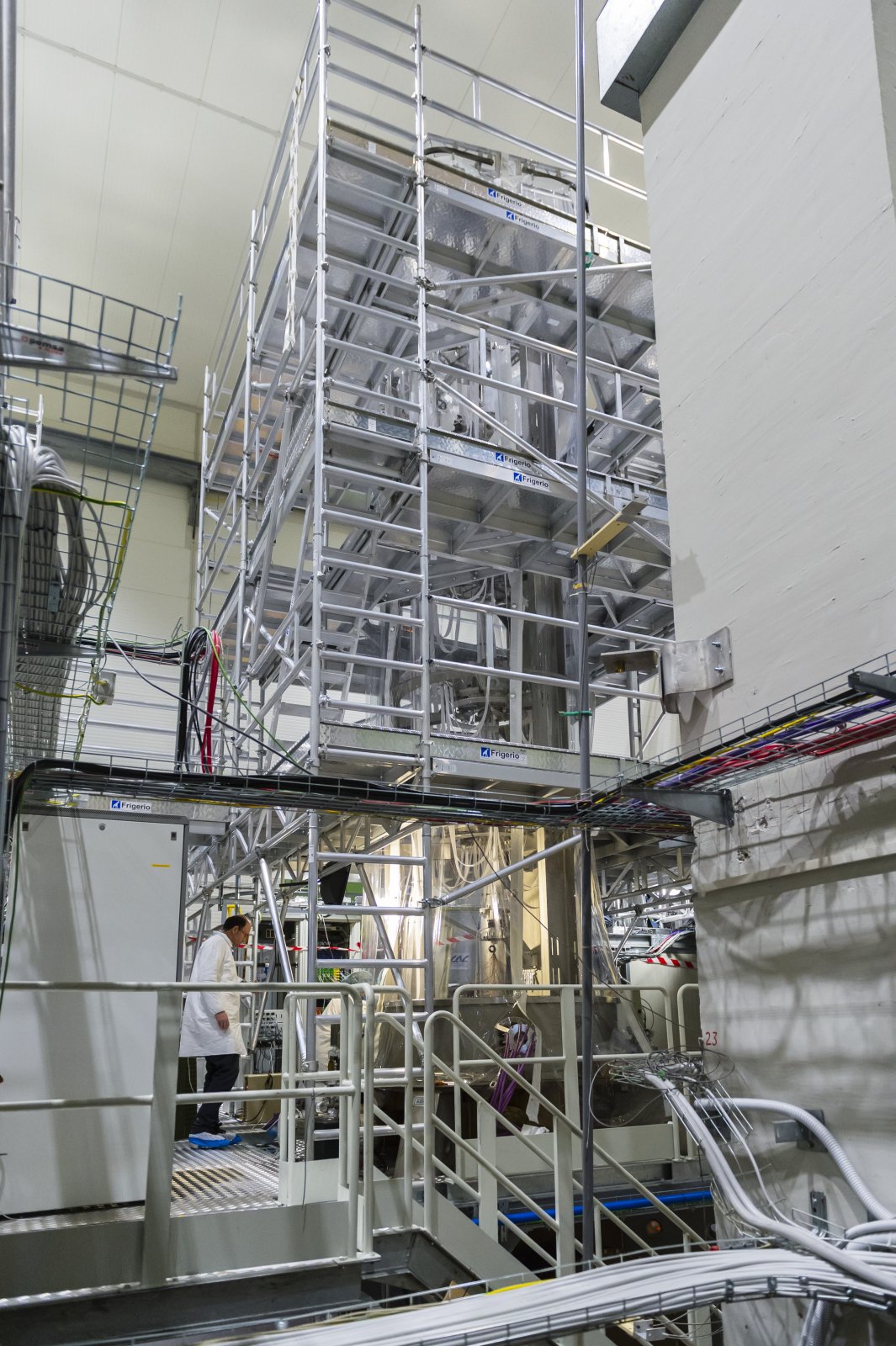
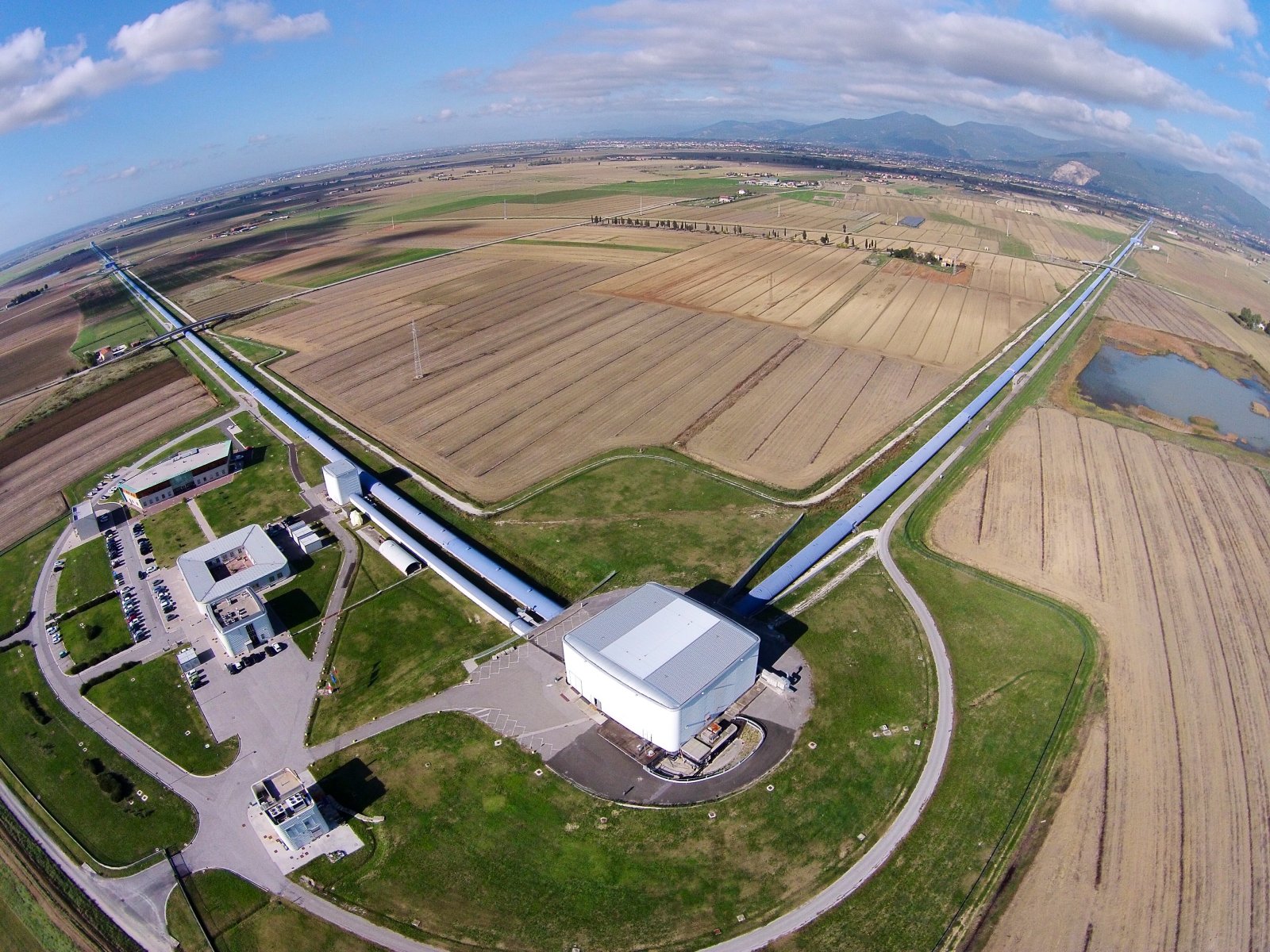
North tube of Virgo
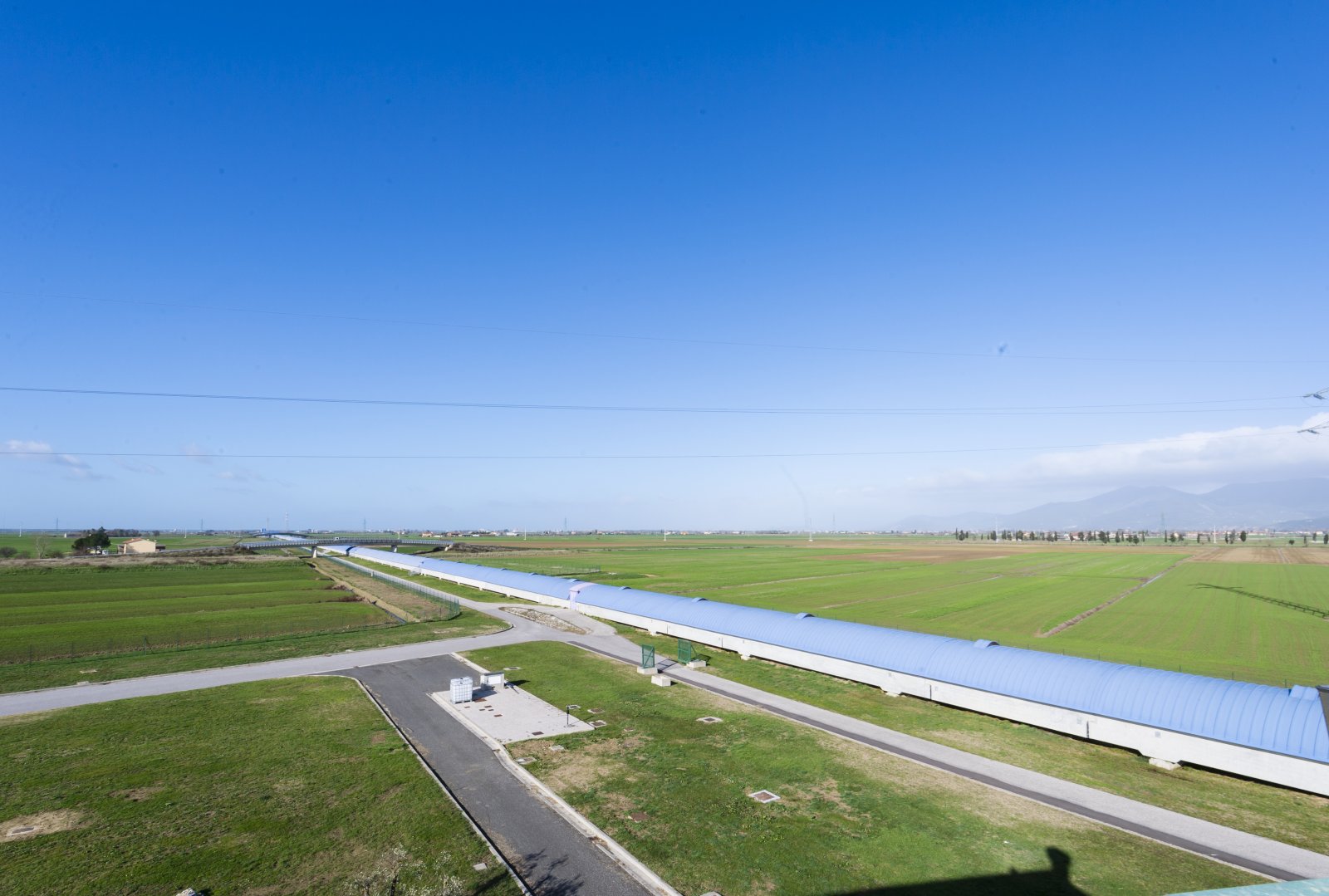

The 3-km long building of Virgo hosts a vacuum tube of 1.3 m of diameter. The laser beam propagates back and forth inside this tube.
Credits: Cyril Frésillon/Virgo/Photothèque CNRS
Album: Instruments – Infrastructures
Tags: